Frame extraction
This initial phase involves extracting individual frames from the continuous video file. It’s like pausing the video at mulitple points and taking snapshots to use for further analysis.

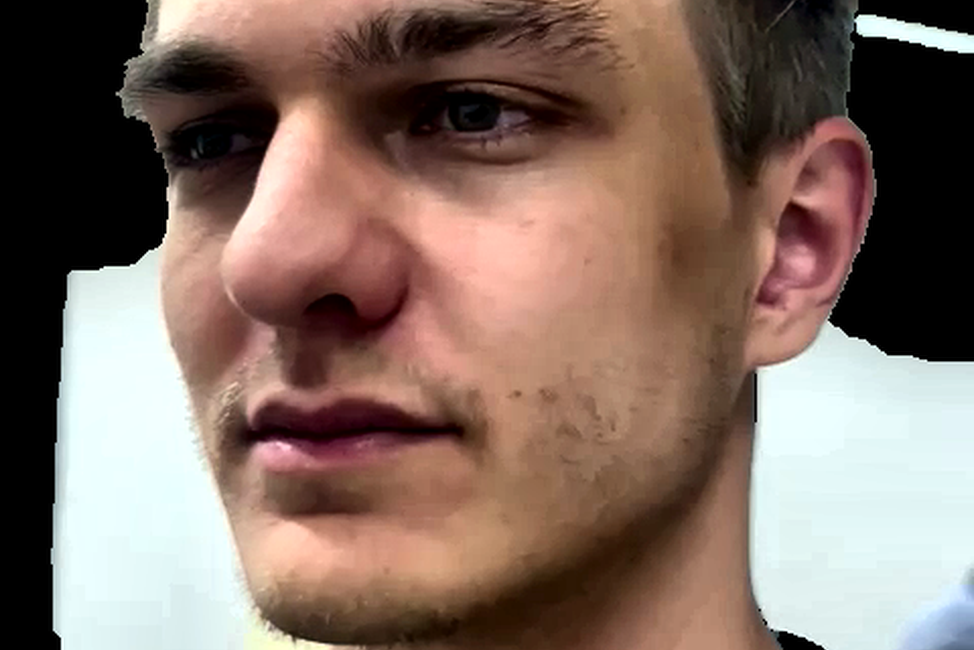
Pre-Processing
Pre-processing enhances the quality of the extracted frames. This step might adjust the lighting, contrast, or remove noise, ensuring that the details necessary for accurate face detection are preserved.

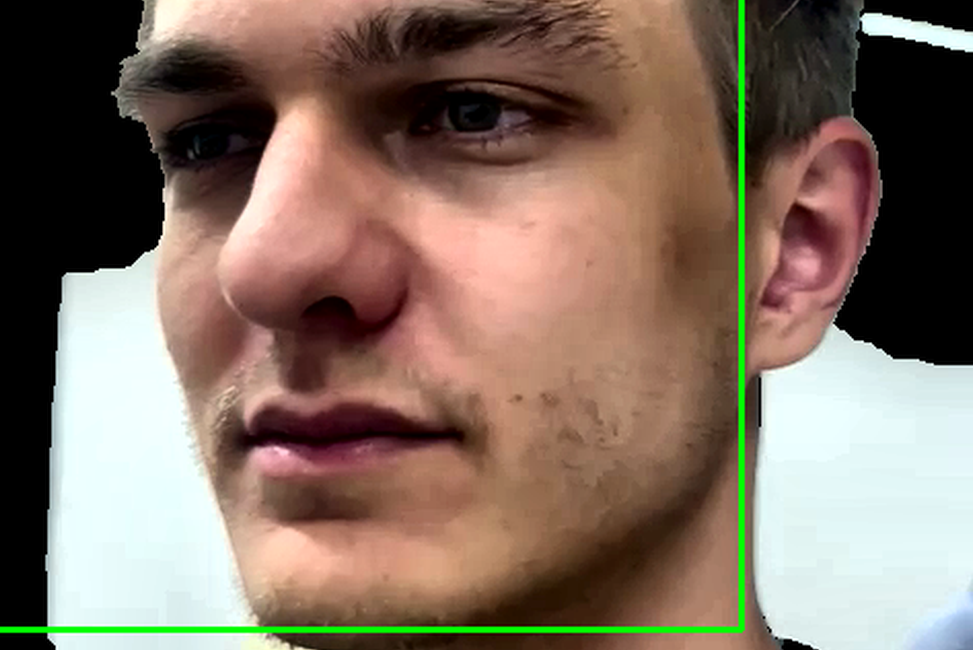
Face Detection and Cropping
In this phase, the program identifies the presence of faces in each frame and isolates them by cropping out everything but the face. This focus ensures higher accuracy in the subsequent stages.

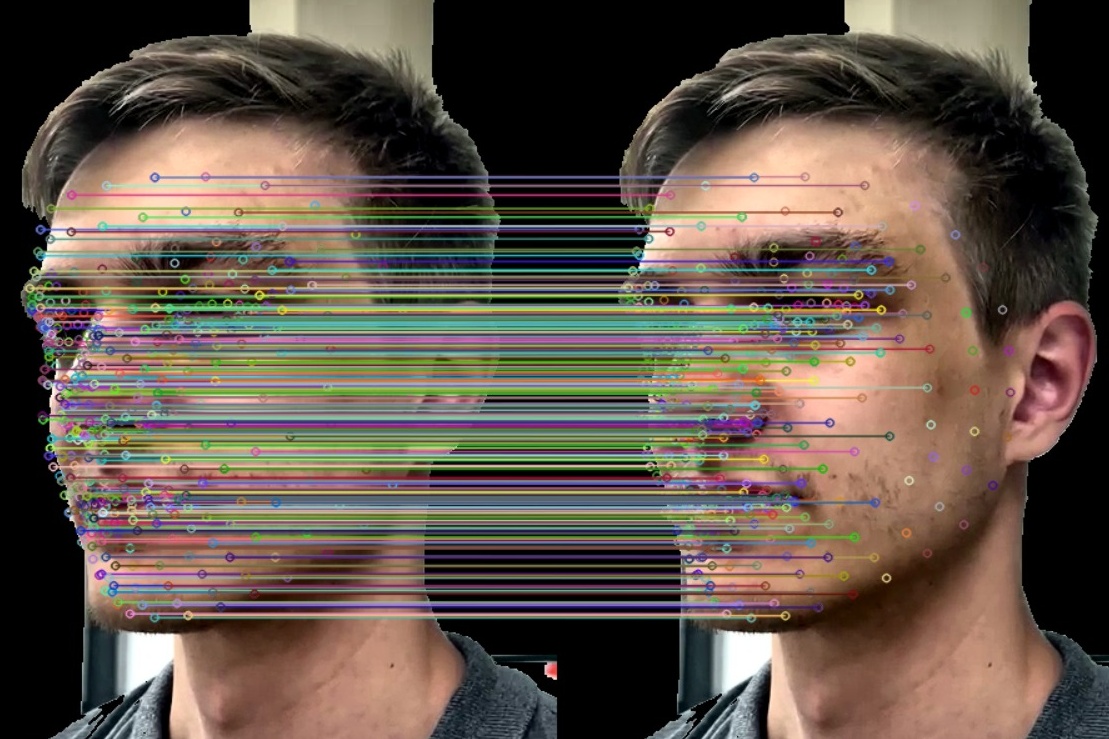
Feature Detection
Feature detection identifies key points of interest on the face, such as the eyes, nose, and mouth corners. These distinctive points are crucial for building the 3D model.
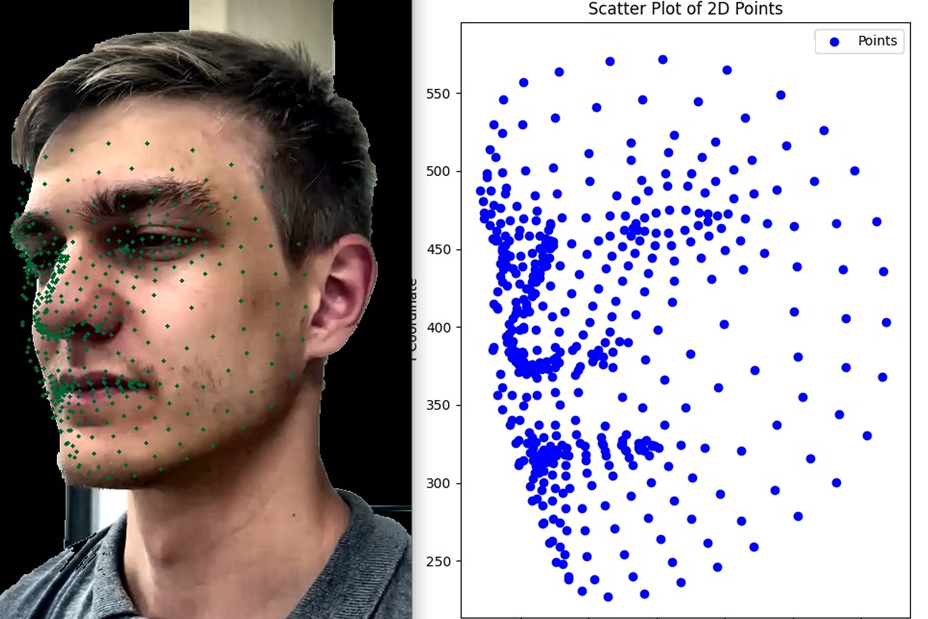
Feature Matching
The software compares features identified across multiple frames to find matches. By understanding how these points link across frames, the program begins to perceive depth.

Camera Position Estimation
Here, the program calculates the position of the camera for each frame, based on the identified features. Knowing how the camera angle changes helps in understanding the face shape.
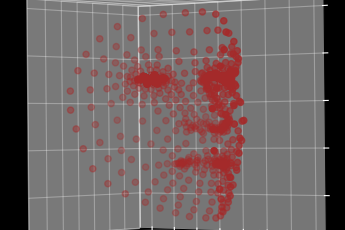
Sparse 3D Cloud Reconstruction
Using information from previous steps, the software constructs a preliminary 3D model, known as a “sparse” cloud, comprising dots representing the key facial features in 3D.
Dense 3D Cloud Reconstruction
This phase enhances the preliminary model using Multi-View Stereo techniques, adding more points to the cloud. It fills in gaps, creating a “dense” cloud for a better representation.
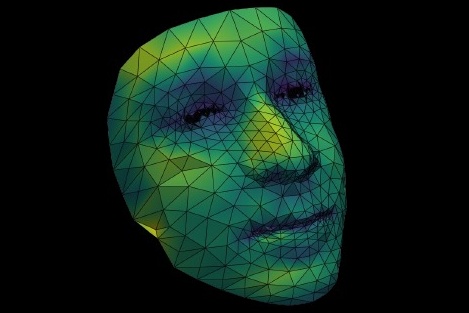
3D Cloud Visualization
Finally, the deailed 3D point cloud is rendered into a comprehensive model. You can rotate, zoom, and interact with this lifelike digital version of the original face and export it to Unreal Engine 5.




